Products
PIRIMICARB
Insecticide
carbamate
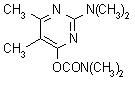
NOMENCLATURE
Common name pirimicarb (BSI, E-ISO, ANSI, JMAF); pirimicarbe
((m) F-ISO); pyrimicarbe (France)
IUPAC name 2-dimethylamino-5,6-dimethylpyrimidin-4-yl
dimethylcarbamate
Chemical Abstracts name 2-(dimethylamino)-5,6-dimethyl-4-pyrimidinyl
dimethylcarbamate
CAS RN [23103-98-2] EEC no. 245-430-1 Development
codes PP062 (ICI) Official codes ENT
27 766; OMS 1330
PHYSICAL CHEMISTRY
Composition Tech. material is 95% pure. Mol.
wt. 238.3 M.f. C11H18N4O2 Form White
solid. M.p. 91.6 °C V.p. 4 ´ 10-1 mPa
(20 °C, by interpolation) KOW logP
= 1.7 (unionised) Henry 3.6 ´ 10-5 Pa
m3 mol-1 (calc.) S.g./density 1.18
(25 °C); tech. 1.21 (25 ºC) Solubility In
purified water 3.0 g/l (20 ºC). In acetone, methanol, xylene >200
g/l (20 ºC). Stability Stable under normal
storage conditions for more than 2 years. Hydrolytically stable at
pH 4-9 (25 °C). Aqueous solutions are unstable to u.v. light; DT50 <1
d (pH 5, 7 or 9). pKa 4.44 (20 °C), weak
base
COMMERCIALISATION
History Aphicide reported by F. L. C. Baranyovits & R.
Ghosh (Chem. Ind. (London), 1969, p. 1018). Introduced by
ICI Plant Protection Division (now Syngenta AG) and first marketed
in 1970. Patents GB 1181657 Manufacturers Jiangsu;
Syngenta
APPLICATIONS
Biochemistry Cholinesterase inhibitor. Mode of action Selective systemic insecticide with contact, stomach, and respiratory action. Absorbed by the roots, and translocated through the xylem. Penetrates the leaves, but is not translocated extensively. Uses A selective aphicide used in a wide range of crops, including cereals and oilseeds (at 125-250 g/ha), potatoes and other vegetables (at 125-375 g/ha), fruit (at 250-750 g/ha), ornamentals and other non-food uses (at 50-500 g/ha). Effective against organophosphorus-resistant Myzus persicae. Formulation types AE; DP; EC; FU; WG; WP.
