Products
DIURON
Herbicide: urea
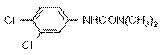
NOMENCLATURE
Common name diuron (BSI, E-ISO, (m) F-ISO, ANSI, WSSA); DCMU
(JMAF); dichlorfenidim* (former exception, USSR)
IUPAC name 3-(3,4-dichlorophenyl)-1,1-dimethylurea
Chemical Abstracts name N'-(3,4-dichlorophenyl)-N,N-dimethylurea
CAS RN [330-54-1] EEC no. 206-354-4 Development
codes DPX 14740 (Du Pont)
PHYSICAL CHEMISTRY
Mol. wt. 233.1 M.f. C9H10Cl2N2O Form Colourless
crystals. M.p. 158-159 ºC V.p. 1.1 ´ 10-3 mPa
(25 ºC) KOW logP = 2.85?.03 (25 ºC) Henry
7.04 ´ 10-6 Pa m3 mol-1 (calc.) S.g./density
1.48 Solubility In water 36.4 mg/l (25 ºC). In acetone 53,
butyl stearate 1.4, benzene 1.2 (all in g/kg, 27 ºC). Sparingly
soluble in hydrocarbons. Stability Stable in neutral media at
normal temperatures, but hydrolysed at elevated temperatures. Hydrolysed
by acids and alkalis. Decomposes at 180-190 ºC.
APPLICATIONS
Biochemistry Photosynthetic electron transport inhibitor at
the photosystem II receptor site. Mode of action Systemic herbicide,
absorbed principally by the roots, with translocation acropetally in
the xylem. Uses Total control of weeds and mosses on non-crop
areas, at 10-30 kg a.i./ha. Selective control of germinating grass
and broad-leaved weeds in many crops, including asparagus, tree fruit,
bush fruit, citrus fruit, vines, olives, pineapples, bananas, sugar
cane, cotton, peppermint, alfalfa, forage legumes, cereals, maize,
sorghum, and perennial grass-seed crops, at 0.6-4.8 kg/ha. Phytotoxic
residues in soil disappear within 1 season at these lower rates. Formulation
types SC; WP.
